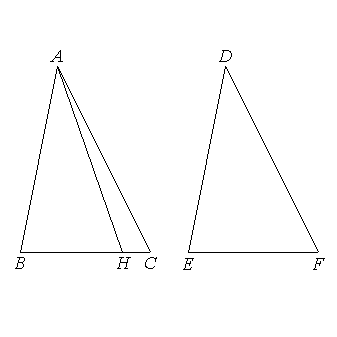H
E
E
L
E
M
E
N
T
S
the two sides AB, BH are equal to the two sides DE, EF respectively; and they contain equal angles;
therefore the base AH is equal to the base DF, and the triangle ABH is equal to the triangle DEF, and the remaining angles will be equal to the remaining angles, namely those which the equal sides subtend; [I.4] therefore
the angle BHA is equal to the angle EFD.
But
the angle EFD is equal to the angle BCA;
therefore
in the triangle AHC, the exterior angle BHA is equal to the interior and opposite angle BCA: which is impossible. [I.16]
Therefore BC is not unequal to EF,